论文部分
Abstract
我们提出一种新的生成对抗网络的训练方式。一个关键的想法是渐进地同时增长生成器和判决器:从一个低分辨率开始, 随着训练的进行, 我们增加了新的层对越来越精细的细节建模。这不仅加速了训练,也使训练更加稳定, 允许我们产生前所未有质量的图片, 比如产生1024像素的CelebA图像。我们也提出了一种增加生成图像的多样性的方式, 在无监督的CIFAR10中取得了创纪录的8.80的得分。此外,我们描述了一些实现细节,这些细节对于阻止生成器和鉴别器之间的不健康竞争非常重要。最后,我们同时在图像质量和多样性上提出了一种评估GAN结果的标准。作为一个额外的贡献, 我们构建了一个更高质量的CelebA数据集的版本。
Introduction
从高维数据分布(例如图像)产生新颖样本的生成方法正在广泛使用,例如语音合成, 图像到图像的翻译, 以及油画风格的图像。目前最突出的方法是自回归模型, 变分自编码器和生成对抗网络。现在它们有明显的优点和缺点。自回归模型,比如PixelCNN, 会生成清晰的图像,但评估速度较慢,并且没有隐表征,因为它们直接对像素上的条件分布进行建模,从而可能限制其适用性。VAEs容易训练但是易于产生模糊的结果由于模型的限制, 尽管最近的作品提升了它。GANs产生清晰的图像,尽管只有很小的分辨率并且变化有限, 并且训练逐渐变得不稳定尽管最近有进步。杂交的方式结合了三者的优点, 但是目前落后于GANs的图像质量。
通常,一个GAN由两个网络组成,生成器和判决器。生成器产生一个样本,比如一张图像,从一个隐编码, 并且理想情况下,这些图像的分布应该与训练分布没有区别。由于通常无法设计出一种功能来分别是否生成图像的分布和训练分布一致,因此需要训练判决器网络来进行评估, 并且由于网络是可微的, 所以我们还得到一个梯度,可以用来将两个网络导向正确的方向。通常,我们的主要关注点是生成器,判决器是一个自适应的损失函数,一旦生成器训练好好就会抛弃它。
这个公式存在很多潜在问题。 当我们测量生成分布和训练分布之间的距离时,如果分布没有大量的重叠(即太容易区分), 则梯度可以指向或多或少的随机方向。起初,JS散度被用作一个距离度量, 最近这个公式被改善了,并且大量的稳定的可替代方式被提出,包括最小二乘法,Wasserstein距离等。我们的投稿在很大程度上与正在进行的讨论正交,我们主要使用改进的Wasserstein损失,但也尝试使用最小二乘损失。
高分辨率图像的生成是很困难的, 因为该分辨率使得生成的图像可以轻易地从训练集中分辨出来, 因此大幅地放大了梯度问题。高分辨率由于内存限制也必须使用小的批数据,更妥协了训练的稳定性。我们的主要见解是,我们可以从更简单的低分辨率图像开始逐步增加生成器和判决器,并添加新层,以随着训练的进行而引入更高分辨率的细节。在高分辨率中,这很大程度上加速了训练并提升了稳定性,我们将会在第二部分进行讨论。
GAN公式并不明确要求由生成的生成模型表示整个训练数据分布。传统观点认为,图像质量和变化之间需要权衡取舍,但是这种观点最近受到了挑战。 多样性的保留程度目前正受到关注,并提出了各种测量方法,包括初始评分,多尺度结构相似(MS-SSIM)等。我们将在第3部分中描述促进多样性的方法,并在第5部分中提出评估质量和多样性的新指标。
4.1部分讨论了对初始化网络的一个微小的修改, 从而使不同层的学习速度更加平衡。此外,在一打minibatch的过程中,传统地, GAN易于迅速发生模式崩溃。通常,它们在判决器饱和开始, 导致非常大的梯度, 随之而来的是不健康的竞争,两个网络中的信号幅度都在增加。我们提出了一种机制,可以阻止生成器参与此类加速,从而解决问题(4.2部分)。
我们使用CelebA, LSUN, CIFAR10数据集上评估我们的投稿。我们提高了CIFAR10的最佳公开的初始评分。由于基准化生成方法中常用的数据集仅限于较低的分辨率,我们也创建了一个高质量的CelebA数据集版本, 该数据集可以进行高达1024x1024像素的输出分辨率的实验。
PROGRESSIVE GROWING OF GANS
我们主要的贡献是一种GANs的训练方式, 我们开始用一个低分辨率的图像, 然后逐渐增加分辨率,通过如图1所示的给网络增加层的方式。这种渐进的性质使训练能够首先发现图像分布的大规模结构,然后将注意力转移到越来越精细的细节上,而不是必须同时学习所有规模。
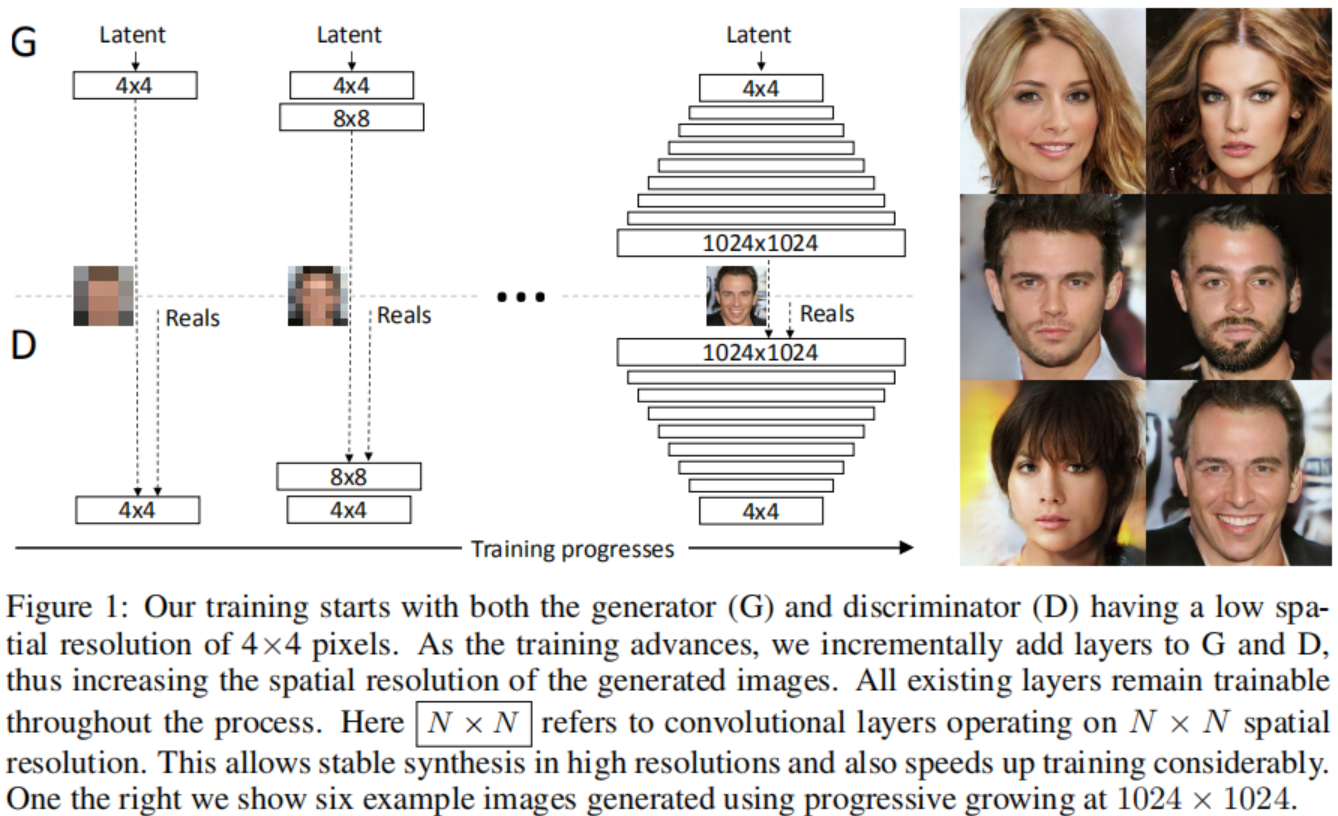
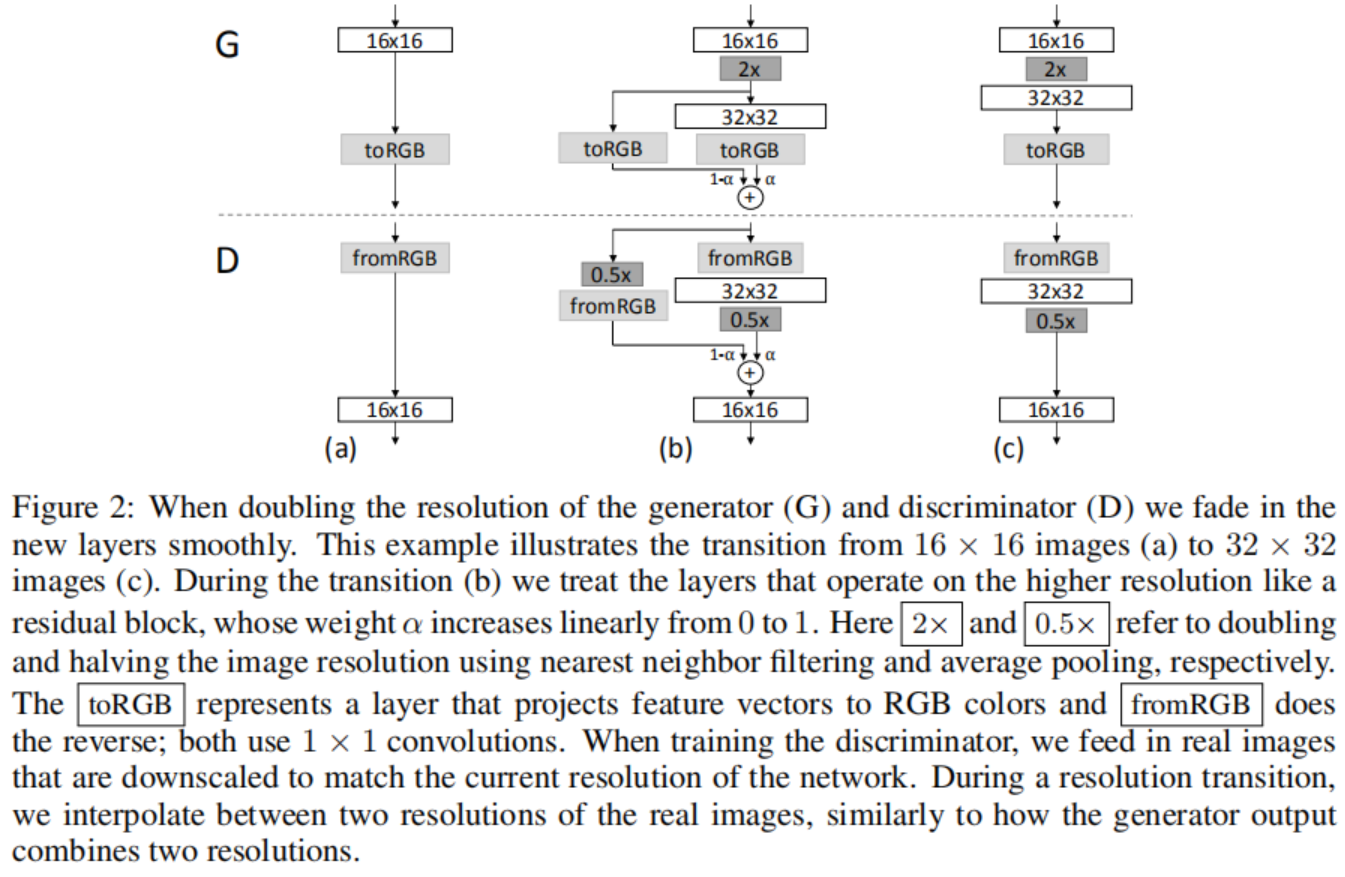
我们使用互为镜像的生成器和判决器网络,并且始终同步增长。 在整个训练过程中,两个网络中所有现有的层均保持可训练状态。当新的层加入网络后, 我们平滑地消退它们, 如图2所示。 这避免了突然影响已经训练好的网络,小分辨率的层。附录A描述了细节上生成器和判决器的结构, 以及其它训练参数。
我们观察到渐进式的训练有几个好处。早期的时候,更小的图像的生成更加稳定因为有更少的分类信息和更少的模式。通过一点一点地增加分辨率我们不断地问一个更简单的问题相比于直接发现一个从隐向量到1024x1024分辨率图像的映射。在实践中, 这种方式足以稳定训练, 使我们能够可靠地使用WGAN-GP损失合成百万像素级图像。
另外一个好处是减少训练时间。随着GAN的不断增长,大多数迭代都是在较低的分辨率下完成的,根据最终输出分辨率的不同,通常可提高2-6倍的速度。
渐进增长的想法源自Wang等的作品, 他们使用多个判决器,这些判决器在不同空间分辨率上操作。这个作品的想法又来自于Durugkar等人的作品,他们同时使用了一个生成器和多个判决器。Ghosh等人做了相反的操作,他们使用多个生成器和一个判决器。按等级划分的GANs(Denton et al., 2015; Huang et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2017)为每一个图像金字塔的等级定义一个生成器和一个判决器。这些方法建立在一个基础上,这个基础和我们的观察结果一致——即从隐向量到高分辨率图像的复杂映射逐步学习更容易——但是关键的不同在于,我们只有一个GAN而不是按等级划分的GAN。我们只是推迟引入已经提前配置好的层。从这个意义上讲,我们的方法类似于自编码器的分层训练。
INCREASING VARIATION USING MINIBATCH STANDARD DEVIATION
GAN有一个倾向是仅仅捕获训练数据中发现的变量的子集,Salimans等人提出“minibatch discrimination”作为一种解决方案。他们不光计算来自于单个图像的特征统计,还计算跨整个批数据的特征统计,因此鼓励生成的小批次和训练图像展现出相似的统计信息。实现方法是在判决器的最后加上一个小批次层,该层学习一个大张量,该张量将输入激活投影到一组统计信息中。 在一个小批数据中,为每个示例生成一组单独的统计数据,并将其连接到层的输出,以便判决器可以在内部使用统计信息。我们大大简化了这种方法,同时也改善了多样性。
我们的简化方案是既没有可学习的参数也没有新的超参数,在一个小批数据的每个空间位置, 我们首先为每个特征计算标准差。 然后,我们对所有特征和空间位置的这些估计值求平均,以得出单个值。我们复制该值并将其连接到所有空间位置以及整个小批量上,从而生成一个附加的(恒定的)特征图。这个层可以被插在判决器的任意位置, 但是我们发现它插在最后的时候效果最好(附录A.1有更多的细节)。我们尝试了更丰富的统计数据,但无法进一步改善多样性。
多样性问题的可替代的解决方案包括展开判决器(Metz et al., 2016)来正则化它的更新, 以及一个“排斥正则化” (Zhao et al., 2017)给生成器增加了一个新的损失项, 在一个小批数据中尽力鼓励它对特征向量进行正交。Ghosh等人的多生成器也服务于一个相似的目标。我们承认这些方法可能比我们的方案增加的多样性还多——或者有可能和它正交——但具体的比较留到以后再说。
NORMALIZATION IN GENERATOR AND DISCRIMINATOR
由于两个网络之间的不健康的竞争,GANs易于扩大信号规模。大多数早期的解决方案通过在生成器中使用BatchNorm的变体来阻止这种情况, 而且也通常在判决器中使用。 这些归一化方法最初是为了消除协变量偏移。然而,我们并有在GANs中观察到这个问题, 因此我们相信GANs中真正需要的是限制信号的规模和竞争。对这两个部分的组成,我们使用了一个不同的方式,它们都不需要可学习的参数。
EQUALIZED LEARNING RATE
我们不像现在流行的趋势那样谨慎的权重初始化, 而是使用N(0,1)分布初始化, 然后在运行时直接放缩权重。确切地说,我们设置$\hat w_i = w_i / c$,其中$w_i$是权重, c是来自何凯明的初始化的每层的规范化常数。动态而不是在初始化期间执行此操作的好处有些微妙,并且与常用的自适应随机梯度下降方法(如RMSProp和Adam)中的尺度不变性有关。这些方法通过估计的标准差对梯度更新进行规范化化,从而使更新独立于参数的尺度。结果,如果一些参数比其它参数有更大的动态范围, 它们将会花更长时间来调整。这是现在初始化引起的现象, 因此有可能学习率同时很大和很小。我们的方式确保这个动态范围,并且因此学习速度,对所有权重来说是相同的。
PIXELWISE FEATURE VECTOR NORMALIZATION IN GENERATOR
禁止由于竞争而使生成器和判决器的规模螺旋失控的情况,我们在每个卷积层之后将每个像素中的特征向量规范化为生成器中的单位长度。我们使用“本地响应标准化”的变体, 令$b_{x, y} = a_{x, y}/\sqrt {\frac{1}{N}\sum_{j=0}^{N-1}(a_{x, y}^j)^2 + \epsilon}$, 其中$\epsilon = 10^{-8}$, N是特征映射的数量,$a_{x, y}$和$b_{x, y}$分别是原始的和规范化后像素的特征向量。我们感到惊讶的是,这种沉重的约束似乎丝毫没有损害生成器, 并且事实上大多数数据集并没有改变结果太多, 但是它非常有效地避免了扩大信号规模。
MULTI-SCALE STATISTICAL SIMILARITY FOR ASSESSING GAN RESULTS
为了比较一个GAN和另一个的结果, 需要调研大量的图片,这是非常乏味的, 困难的,主观的。因此需要依赖于自动的方式从大量的图像集里计算一些指标。我们注意到现存的方式比如MS-SSIM发现大规模的模式崩溃, 但是不能对小的影响(比如颜色或纹理变化的损失)作出反应,并且它们也没有直接评估与训练集相似度这一项的图像质量。
我们基于直觉, 即成功的生成器生成的样本的图片结构和训练集在所有尺度上都相似。我们建议通过考虑采样自生成图像和目标图像拉普拉斯金字塔的局部图像块的分布之间的多尺度统计相似度, 来研究此问题, 从16x16像素的低分辨率开始。按照标准惯例,金字塔会逐渐加倍,直到达到完整分辨率为止,每个连续级别将差异编码为前一个级别的上采样版本。
单个拉普拉斯金字塔等级对应于特定的空间频带。我们随机采样16384张图像并且提取128个来自拉普拉斯金字塔每层的描述子, 总共每层$2^{21}$个描述子。每个描述子3个通道7x7像素, 表示为$x \in R^{7 \times 7 \times 3} = R^{147}$。我们将训练集第l级的区域和生成集的区域分别表示为\(\{x_i^l\}_{i=1}^{2^{21}}\)和\(\{y_i^l\}_{i=l}^{2^{21}}\)。我们首先规范化\(\{x_i^l\}\)和\(\{y_i^l\}\)每个通道的均值和方差,然后通过使用512个映射计算它们的分片Wasserstein距离(\(x_i^l\)和\(y_i^l\))估计统计信息的相似度, 该距离可有效的可计算的推土机距离随机近似值。
直观地讲,Wasserstein距离很小,表明色块的分布相似, 意味着训练图像和生成的图像在这个空间分辨率上外观和多样性都十分相似。特别是,从分辨率最低的16×16图像中提取的色块集之间的距离表示大规模图像结构中的相似性,而最高级的色块则编码有关像素级属性(如边缘的清晰度和噪声)的信息。
Appendix
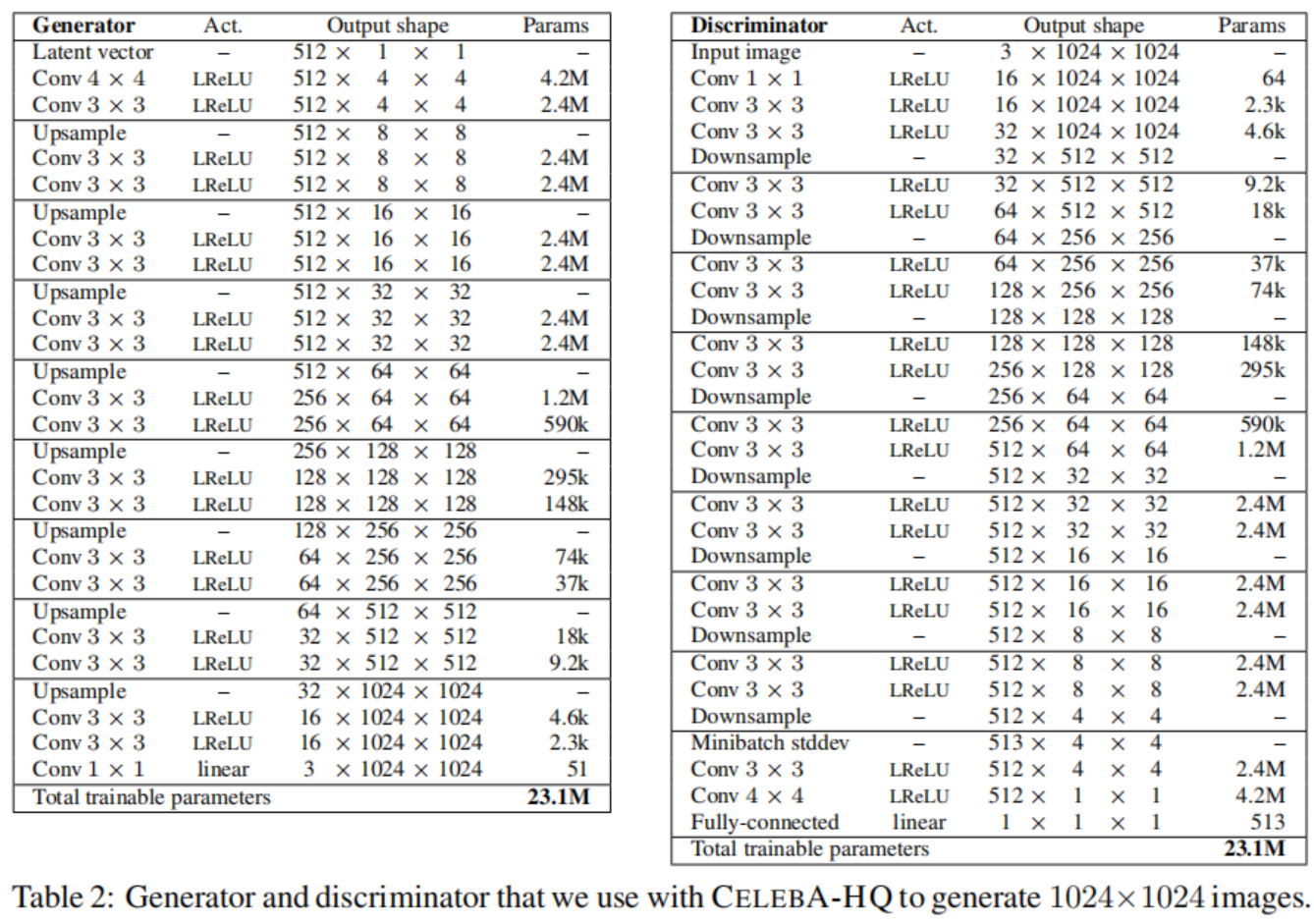
1024 × 1024 NETWORKS USED FOR CELEBA-HQ
表2展示了我们在CelebA-HQ数据集上使用的全分辨率的生成器和判决器的网络结构。这两个网络主要由重复的3层模块组成,我们在训练过程中一一介绍。生成器的最后一层1x1的卷积层和图2中的toRGB相关, 判决器的第一个1x1卷积层和生成器相似,与fromRGB相关。我们从4x4的分辨率开始,训练网络直到我们向判决器展示了总共800K的真实图像。我们然后在两个阶段切换:在接下来的800K图片中褪去前三层的块, 用800K图片稳定网络, 在接下来800K图片中褪去接下来三层的块, 以此类推。
我们的潜在向量对应于512维超球面上的随机点,我们表示训练和生成的图像在[-1,1]之间。我们在两个网络所有层中使用值为0.2的Leaky ReLU, 除了最后一层使用线性激活。我们没有使用BatchNorm, LayerNorm或者WeightNorm,但是我们对生成器的每次3x3卷积之后的特征向量使用了在4.2部分所说的像素级别的规范化。我们初始化所有的偏差参数为0,所有的权重根据单位方差的正态分布初始化。然而,我们在运行时用如4.1部分所说的特别的常数层放缩权重。如第三部分所说,我们在判决器的最后注入跨小批量标准差作为4x4分辨率的额外的特征映射。表2中的上采样和降采样操作分别使用2x2元素复制和平均池化。
我们使用Adam来训练网络, 参数为$\alpha=0.001, \beta_1=0, \beta_2=0.99, \epsilon=10^{-8}$。我们不使用任何学习率下降或上升, 但是为了在训练过程中给任意点可视化生成器输出, 我们对衰减为0.999的生成器使用指数运行平均值。在分辨率为$4^2-128^2$时, 我们使用批大小为16, 当分辨率为$256^2$时减小到14, $512^2 \rightarrow 6$, $1024^2 \rightarrow 3$避免超出可用的内存预算。我们使用WGAN-GP损失, 但是不像Gulrajani等人那样,我们会在每个小批量的基础上优化生成器和区分器之间进行交替,即我们将$n_{critic}$设置为1。此外,我们给判决器的损失引入了一个第四项, 它是一个极小的权重保证判决器的输出不会偏离零太远。更精确地讲,我们让$L’ = L + \epsilon_{drift}E_{x \in P_r}[D(x)^2]$, 其中$\epsilon_{drift}=0.001$。
每当我们需要以低于1024×1024的空间分辨率进行操作时,我们都通过在两个网络中保留适当数量的复制的3层块副本来做到这一点。
实现部分
导入相关包
1
2
3
4
5
6
import torch
import timeit
import os
import time
import copy
import numpy as np
生成器
学习率均等化的卷积层和反卷积层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# extending Conv2D and Deconv2D layers for equalized learning rate logic
class _equalized_conv2d(torch.nn.Module):
""" conv2d with the concept of equalized learning rate
Args:
:param c_in: input channels
:param c_out: output channels
:param k_size: kernel size (h, w) should be a tuple or a single integer
:param stride: stride for conv
:param pad: padding
:param bias: whether to use bias or not
"""
def __init__(self, c_in, c_out, k_size, stride=1, pad=0, bias=True):
from torch.nn.modules.utils import _pair
from numpy import sqrt, prod
super(_equalized_conv2d, self).__init__()
# define the weight and bias if to be used
self.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.nn.init.normal_(torch.empty(c_out, c_in, *_pair(k_size))))
self.use_bias = bias
self.stride = stride
self.pad = pad
if self.use_bias:
self.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(c_out).fill_(0))
# prod 计算所有元素的积,可以指定维度
# scale为什么这么算?
fan_in = prod(_pair(k_size)) * c_in
self.scale = sqrt(2) / sqrt(fan_in)
def forward(self, x):
from torch.nn.functional import conv2d
return conv2d(input=x,
weight=self.weight * self.scale,
bias=self.bias if self.use_bias else None,
stride=self.stride,
padding=self.pad)
# 输出的是各层权重的形状
def extra_repr(self):
return ",".join(map(str, self.weight.shape))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
class _equalized_deconv2d(torch.nn.Module):
""" Transpose convolution using the equalized learning rate
Args:
:param c_in: input channels
:param c_out: output channels
:param k_size: kernel size
:param stride: stride for convolution transpose
:param pad: padding
:param bias: whether to use bias or not
"""
def __init__(self, c_in, c_out, k_size, stride=1, pad=0, bias=True):
""" constructor for the class """
from torch.nn.modules.utils import _pair
from numpy import sqrt
super(_equalized_deconv2d, self).__init__()
# define the weight and bias if to be used
self.weight = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.nn.init.normal_(torch.empty(c_in, c_out, *_pair(k_size))))
self.use_bias = bias
self.stride = stride
self.pad = pad
if self.use_bias:
self.bias = torch.nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(c_out).fill_(0))
fan_in = c_in # value of fan_in for deconv
self.scale = sqrt(2) / sqrt(fan_in)
def forward(self, x):
from torch.nn.functional import conv_transpose2d
return conv_transpose2d(input=x,
weight=self.weight * self.scale,
bias=self.bias if self.use_bias else None,
stride=self.stride,
padding=self.pad)
def extra_repr(self):
return ",".join(map(str, self.weight.shape))
像素级别的规范化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
#----------------------------------------------------------------
# Pixelwise feature vector normalization.
#reference:https://github.com/tkarras/progressive_growing_of_gans/blob/master/networks.py#L120
#----------------------------------------------------------------
class PixelwiseNorm(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(PixelwiseNorm, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x, alpha=1e-8):
# [N1HW], 对三个通道求均值,三个通道压缩成了单个通道
y = x.pow(2.).mean(dim=1, keepdim=True).add(alpha).sqrt()
# 带有广播机制,应该对图片的每个像素都除了一个均值
y = x / y
return y
生成器初始化块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
# ==========================================================
# Layers required for Building The generator and
# discriminator
# ==========================================================
class GenInitialBlock(torch.nn.Module):
""" Module implementing the initial block of the input """
def __init__(self, in_channels, use_eql):
"""
constructor for the inner class
:param in_channels: number of input channels to the block
:param use_eql: whether to use equalized learning rate
"""
from torch.nn import LeakyReLU
super(GenInitialBlock, self).__init__()
if use_eql:
self.conv_1 = _equalized_deconv2d(in_channels, in_channels, (4, 4), bias=True)
self.conv_2 = _equalized_conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, (3, 3), pad=1, bias=True)
else:
from torch.nn import Conv2d, ConvTranspose2d
self.conv_1 = ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, in_channels, (4, 4), bias=True)
self.conv_2 = Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, (3, 3), padding=1, bias=True)
self.pixNorm = PixelwiseNorm()
self.lrelu = LeakyReLU(0.2)
def forward(self, x):
# 在前面加两维度
y = torch.unsqueeze(torch.unsqueeze(x, -1), -1)
# 先升采样再降采样?为什么这样做?
y = self.lrelu(self.conv_1(y))
y = self.lrelu(self.conv_2(y))
y = self.pixNorm(y)
return y
生成器普通块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
class GenGeneralConvBlock(torch.nn.Module):
""" Module implementing a general convolutional block """
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, use_eql):
from torch.nn import LeakyReLU
from torch.nn.functional import interpolate
super(GenGeneralConvBlock, self).__init__()
self.upsample = lambda x: interpolate(x, scale_factor=2)
if use_eql:
self.conv_1 = _equalized_conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, (3, 3), pad=1, bias=True)
self.conv_2 = _equalized_conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, (3, 3), pad=1, bias=True)
else:
from torch.nn import Conv2d
self.conv_1 = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, (3, 3), padding=1, bias=True)
self.conv_2 = Conv2d(out_channels, out_channels, (3, 3), padding=1, bias=True)
self.pixNorm = PixelwiseNorm()
self.lrelu = LeakyReLU(0.2)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.upsample(x)
y = self.pixNorm(self.lrelu(self.conv_1(y)))
y = self.pixNorm(self.lrelu(self.conv_2(y)))
return y
生成器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
class Generator(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self, depth=7, latent_size=512, use_eql=True):
"""
constructor for the Generator class
:param depth: required depth of the Network
:param latent_size: size of the latent manifold
:param use_eql: whether to use equalized learning rate
"""
from torch.nn import ModuleList
from torch.nn.functional import interpolate
super(Generator, self).__init__()
# 这个trick值得学习,如果是2的n次幂,那么它和自身减一按位与必是0
assert latent_size != 0 and ((latent_size & (latent_size -1))==0), "latent size not a power of 2"
if depth >= 4:
assert latent_size >= np.power(2, depth -4), "latent size will diminish to zero"
self.use_eql = use_eql
self.depth = depth
self.latent_size = latent_size
self.initial_block = GenInitialBlock(self.latent_size, use_eql=self.use_eql)
self.layers = ModuleList([])
if self.use_eql:
self.toRGB = lambda in_channels: _equalized_conv2d(in_channels, 3, (1, 1), bias=True)
else:
from torch.nn import Conv2d
self.toRGB = lambda in_channels: Conv2d(in_channels, 3, (1, 1), bias=True)
self.rgb_converters = ModuleList([self.toRGB(self.latent_size)])
# create the remaining layers
for i in range(self.depth - 1):
if i <= 2:
layer = GenGeneralConvBlock(self.latent_size, self.latent_size, use_eql=self.use_eql)
rgb = self.toRGB(self.latent_size)
else:
layer = GenGeneralConvBlock(
int(self.latent_size // np.power(2, i-3)),
int(self.latent_size // np.power(2, i-2)),
use_eql = self.use_eql
)
rgb = self.toRGB(int(self.latent_size // np.power(2, i-2)))
self.layers.append(layer)
self.rgb_converters.append(rgb)
# register the temporary upsampler
self.temporaryUpsampler = lambda x: interpolate(x, scale_factor=2)
def forward(self, x, depth, alpha):
assert depth < self.depth, "Requested output depth cannot be produced"
y = self.initial_block(x)
if depth > 0:
for block in self.layers[:depth-1]:
y = block(y)
# 旧层
residual = self.rgb_converters[depth-1](self.temporaryUpsampler(y))
# 新层
straight = self.rgb_converters[depth](self.layers[depth - 1](y))
out = (alpha * straight) + ((1 - alpha) * residual)
else:
out = self.rgb_converters[0](y)
return out
判决器
批标准差添加给判决器的特征
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
class MinibatchStdDev(torch.nn.Module):
"""
Minibatch standard deviation layer for the discriminator
"""
def __init__(self):
super(MinibatchStdDev, self).__init__()
def forward(self, x, alpha=1e-8):
"""
forward pass of the layer
:param x: input activation volume
:param alpha: small number for numerical stability
:return: y => x appended with standard deviation constant map
"""
batch_size, _, height. width = x.shape
# [B x C x H x W] Subtract mean over batch.
y = x - x.mean(dim=0, keepdim=True)
# [1 x C x H x W] Calc standard deviation over batch
# y.pow: 方差 --> sqrt: 标准差 --> 对batch求均值,Minibatch的标准差
y = torch.sqrt(y.pow(2.).mean(dim=0, keepdim=False) + alpha)
# 所有batch,所有通道,所有像素点的平均标准差
y = y.mean().view(1, 1, 1, 1)
# 将上面求得的标准差广播成[B x 1 x H x W]
y = y.repeat(batch_size, 1, height, width)
# 在通道那一维拼接x和y
y = torch.cat([x, y], 1)
return y
判决器最后一块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
class DisFinalBlock(torch.nn.Module):
""" Final block for the Discriminator """
def __init__(self, in_channels, use_eql):
from torch.nn import LeakyReLU
super(DisFinalBlock, self).__init__()
# declare the required modules for forward pass
self.batch_discriminator = MinibatchStdDev()
if use_eql:
self.conv_1 = _equalized_conv2d(in_channels + 1, in_channels, (3, 3), pad=1, bias=True)
self.conv_2 = _equalized_conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, (4, 4), bias=True)
# final conv layer emulates a fully connected layer
self.conv_3 = _equalized_conv2d(in_channels, 1, (1, 1), bias=True)
else:
from torch.nn import _equalized_conv2d
self.conv_1 = Conv2d(in_channels + 1, in_channels, (3, 3), padding=1, bias=True)
self.conv_2 = Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, (4, 4), bias=True)
# final conv layer emulates a fully connected layer
self.conv_3 = Conv2d(in_channels, 1, (1, 1), bias=True)
self.lrelu = LeakyReLU(0.2)
def forward(self, x):
# minibatch_std_dev layer
y = self.batch_discriminator(x)
y = self.lrelu(self.conv_1(y))
y = self.lrelu(self.conv_2(y))
# fully connected layer
# 原文中用的全连接层,这里用1x1卷积+view替代了
y = self.conv_3(y)
# flatten the output raw discriminator scores
return y.view(-1)
判决器普通块
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
class DisGeneralConvBlock(torch.nn.Module):
""" General block in the discriminator """
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, use_eql):
from torch.nn import AvgPool2d, LeakyReLU
super(DisGeneralConvBlock, self).__init__()
if use_eql:
self.conv_1 = _equalized_conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, (3, 3), pad=1, bias=True)
self.conv_2 = _equalized_conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, (3, 3), pad=1, bias=True)
else:
from torch.nn import _equalized_conv2d
self.conv_1 = Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, (3, 3), padding=1, bias=True)
self.conv_2 = Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, (3, 3), padding=1, bias=True)
self.downSampler = AvgPool2d(2)
self.lrelu = LeakyReLU(0.2)
def forward(self, x):
y = self.lrelu(self.conv_1(x))
y = self.lrelu(self.conv_2(y))
y = self.downSampler(y)
return y
判决器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
#================================================================
# Discriminator Module
# can be used with ProGAN or standalone (for inference).
# Note this cannot be used with ConditionalProGAN
#================================================================
class Discriminator(torch.nn.Module):
""" Discriminator of the GAN """
def __init__(self, height=7, feature_size=512, use_eql=True):
"""
constructor for the class
:param height: total height of the discriminator (Must be equal to the Generator depth)
:param feature_size: size of the deepest features extracted
(Must be equal to Generator latent_size)
:param use_eql: whether to use equalized learning rate
"""
from torch.nn import ModuleList, AvgPool2d
super(Discriminator, self).__init__()
assert feature_size != 0 and ((feature_size & feature_size - 1) == 0), "feature size not a power of 2"
if height >= 4:
assert feature_size >= np.power(2, height-4), "feature size cannot be produced"
self.use_eql = use_eql
self.height = height
self.feature_size = feature_size
self.final_block = DisFinalBlock(self.feature_size, use_eql=self.use_eql)
self.layers = ModuleList([])
if self.use_eql:
self.fromRGB = lambda out_channels: _equalized_conv2d(3, out_channels, (1, 1), bias=True)
else:
from torch.nn import _equalized_conv2d
self.fromRGB = lambda out_channels: Conv2d(3, out_channels, (1, 1), bias=True)
self.rgb_to_features = ModuleList([self.fromRGB(self.feature_size)])
# create the remaining layers
for i in range(self.height - 1):
if i > 2:
layer = DisGeneralConvBlock(
int(self.feature_size // np.power(2, i-2)),
int(self.feature_size // np.power(2, i-3)),
use_eql = self.use_eql
)
rgb = self.fromRGB(int(self.feature_size // np.power(2, i-2)))
else:
layer = DisGeneralConvBlock(self.feature_size,
self.feature_size,
use_eql=self.use_eql)
rgb - self.fromRGB(self.feature_size)
self.layers.append(layer)
self.rgb_to_features.append(rgb)
self.temporaryDownsampler = AvgPool2d(2)
def forward(self, x, height, alpha):
assert height < self.height, "Requested output depth cannot be produced"
if height > 0:
# 旧层
residual = self.rgb_to_features[height-1](self.temporaryDownsampler(x))
# 新层
straight = self.layer[height-1](self.rgb_to_features[height](x))
for block in reversed(self.layers[:height - 1]):
y = block(y)
else:
y = self.rgb_to_features[0](x)
out = self.final_block(y)
return out
更新指数平均权重
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# function to calculate the Exponential moving averages for the Generator weights
# This function updates the exponential average weights based on the current training
def update_average(model_tgt, model_src, beta):
# utility function for toggling the gradient requirements of the models
def toggle_grad(model, requires_grad):
for p in model.parameters():
p.requires_grad_(requires_grad)
# turn off gradient calculation
toggle_grad(model_tgt, False)
toggle_grad(model_src, False)
param_dict_src = dict(model_src.named_parameters())
for p_name, p_tgt in model_tgt.named_parameters():
p_src = param_dict_src[p_name]
assert (p_src is not p_tgt)
p_tgt.copy_(beta * p_tgt + (1. - beta) * p_src)
toggle_grad(model_tgt, True)
toggle_grad(model_src, True)
loss-WGAN-GP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
class GANLoss:
""" Base class for all losses
@args:
dis: Discriminator used for calculating the loss
Note this must be a part of the GAN framework
"""
def __init__(self, dis):
self.dis = dis
def dis_loss(self, real_samps, fake_samps, height, alpha):
raise NotImplementedError("dis_loss method has not been implemented")
def gen_loss(self, real_samps, fake_samps, height, alpha):
raise NotImplementedError("gen_loss method has not been implemented")
class WGAN_GP(GANLoss):
def __init__(self, dis, drift=0.001, use_gp=False):
# 在python3中super().xxx相当于super(Class, self).xxx
super().__init__(dis)
self.drift = drift
self.use_gp = use_gp
def __gradient_penalty(self, real_samps, fake_samps, height, alpha, reg_lambda=10):
batch_size = real_samps.shape[0]
epsilon = torch.rand((batch_size, 1, 1 ,1)).to(fake_samps.device)
merged = epsilon * real_samps + ((1 - epsilon) * fake_samps)
merged.requires_grad_(True)
op = self.dis(merged, height, alpha)
gradient = torch.autograd.grad(
outputs=op,
inputs = merged,
grad_outputs=torch.ones_like(op),
create_graph=True,
retain_graph=True,
only_inputs=True)[0]
gradient = gradient.view(gradient.shape[0], -1)
# 对第二维的梯度求L2范数
penalty = reg_lambda * ((gradient.norm(p=2, dim=1) - 1) ** 2).mean()
return penalty
def dis_loss(self, real_samps, fake_samps, height, alpha):
fake_out = self.dis(fake_samps, height, alpha)
real_out = self.dis(real_samps, height, alpha)
# 我们的目的是real和fake越相近越好,也就是real - fake越小越好
# 而Discriminator的目的是区分real和fake,也就是real - fake越大越好
# 也就是fake-real越小越好
loss = (torch.mean(fake_out) - torch.mean(real_out) + (self.drift * torch.mean(real_out ** 2)))
if self.use_gp:
# gradient penalty使得梯度稳在1-Lipschitz范数
gp = slef.__gradient_penalty(real_samps, fake_samps, height, alpha)
loss += gp
return loss
def gen_loss(self, real_samps, fake_samps, height, alpha):
loss = -torch.mean(self.dis(fake_samps, height, alpha))
return loss
图像预处理
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
def get_transform(new_size=None):
"""
obtain the image transforms required for the input data
:param new_size: size of the resized images
:return: image_transform => transform object from TorchVision
"""
from torchvision.transforms import ToTensor, Normalize, Compose, Resize
if new_size is not None:
image_transform = Compose([
Resize(new_size),
ToTensor(),
Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
else:
image_transform = Compose([
ToTensor(),
Normalize(mean=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5), std=(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
])
return image_transform
def get_data_loader(dataset, batch_size, num_workers):
"""
generate the data_loader from the given dataset
:param dataset: dataset for training (Should be a PyTorch dataset)
Make sure every item is an Image
:param batch_size: batch size of the data
:param num_workers: num of parallel readers
:return: dl => dataloader for the dataset
"""
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
dl = DataLoader(
dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
num_workers=num_workers
)
return dl
预测
引入相关包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
import argparse
import torch
import numpy as np
import os
from torch.backends import cudnn
from torch.nn.functional import interpolate
from tqdm import tqdm
参数初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
# turn on the fast GPU processing mode on
cudnn.benchmark = True
# define the device for the training script
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def parse_arguments():
"""
default command line argument parser
:return: args => parsed command line arguments
"""
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("--generator_file",
type=str,
default="GAN_GEN_8.pth",
help="pretrained weights file for generator")
parser.add_argument("--latent_size",
type=int,
default=512,
help="latent size for the generator")
parser.add_argument("--depth", action="store",
default=9,
help="depth of the network. **Starts from 1")
parser.add_argument("--out_depth",
type=int,
default=6,
help="output depth of images. **Starts from 0")
parser.add_argument("--num_samples",
type=int,
default=300,
help="number of synchronized grids to be generated")
parser.add_argument("--out_dir",
type=str,
default="interp_animation_frames/",
help="path to the output directory for the frames")
args = parser.parse_known_args()[0]
return args
def adjust_dynamic_range(data, drange_in=(-1, 1), drange_out=(0, 1)):
"""
adjust the dynamic colour range of the given input data
:param data: input image data
:param drange_in: original range of input
:param drange_out: required range of output
:return: img => colour range adjusted images
"""
if drange_in != drange_out:
scale = (np.float32(drange_out[1]) - np.float32(drange_out[0])) / (np.float32(drange_in[1]) - np.float32(drange_in[0]))
bias = (np.float32(drange_out[0]) - np.float32(drange_in[0]) * scale)
data = data * scale + bias
return torch.clamp(data, min=0, max=1)
保存图像
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
import torch
from torchvision import transforms
from PIL import Image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import cv2
# loader使用torchvision中自带的transforms函数
loader = transforms.Compose([
transforms.ToTensor()])
unloader = transforms.ToPILImage()
def save_image(tensor, epoch):
image = tensor.cpu().clone() # we clone the tensor to not do changes on it
image = image.squeeze(0) # remove the fake batch dimension
image = unloader(image)
image.save('save_pic/epoch_%d.png'%epoch)
预测
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
args = parse_arguments()
print("Creating generator object ...")
# create the generator object
gen = torch.nn.DataParallel(Generator(
depth=args.depth,
latent_size=args.latent_size
))
print("Loading the generator weights from:", args.generator_file)
# load the weights into it
gen.load_state_dict(
torch.load(args.generator_file, map_location=str(device))
)
#path for saving the files:
save_path = args.out_dir
print("Generating scale synchronized images ...")
for img_num in tqdm(range(1, args.num_samples + 1)):
# generate the images:
with torch.no_grad():
point = torch.randn(1, args.latent_size)
point = (point / point.norm()) * (args.latent_size ** 0.5)
ss_image = gen(point, depth=args.out_depth, alpha=1)
# color adjust the generated image:
ss_image = adjust_dynamic_range(ss_image)
#save the ss_image in the directory
save_image(ss_image, img_num)
print("Generated %d images at %s" % (args.num_samples, save_path))
实验结果
预训练模型的下载地址:
https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1ex27dbFD_4Ycic6P9y3V9i63AvcuAe95

生成的图像颜色很奇怪, 尝试RGB和BGR格式切换也不对。
因为原作者使用scipy的imsave(要求版本1.2.1以下, 而tensorflow要求版本1.4以上)来保存图片,而我使用PIL和opencv保存尝试, 可能这里会导致结果不同?
Reference
- Karras T, Aila T, Laine S, et al. Progressive growing of gans for improved quality, stability, and variation[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.10196, 2017.
- akanimax/pro_gan_pytorch