论文部分
Abstract
我们提出一种新的生成对抗网络的生成器结构,灵感来自于风格迁移。 新的结构可以自动地、无监督地学习分离的高等级的特征(比如当在人脸数据集上训练时的姿势和身份)以及生成图片的随机多样性(比如雀斑,头发等),它可以实现符合直觉地、在特定尺度上生成控制。根据传统的质量分布标准,新的生成器提高了最佳表现, 实现明显更好的插值属性,并且更好地解耦隐变量。为了量化插值质量和解耦程度,我们提出了两个新的,自动的,适用于任何生成器结构的方式。最后, 我们引入了一个新的,高变化度的,高质量的人脸数据集。
1. Introduction
由生成方式产生的分辨率和图像质量——尤其是生成对抗网络(GAN)——最近有快速明显的提升。然而生成器仍然被用作一个黑盒子,尽管最近的一些努力, 仍然缺乏对图像合成过程的变化方面的理解, 比如随机特征的源头。隐空间的属性也没有很好地理解,通常展示的潜空间插值没有提供定量方法来比较不同的生成器。
受风格迁移的启发, 我们重新设计了生成器结构,以一种全新的方式空手指图像的合成过程。我们的生成器开始于一个学习到的常量输入,并且基于隐编码在每个卷积层调整图像的风格, 因此直接在不同尺度控制图像特征的强度。结合上直接注入网络的噪声,这种结构上的变化导致生成图像中的高级属性(例如,姿势,身份)与随机变化(例如,雀斑,头发)自动,无监督地分离, 并实现直观的尺度特定特定混合和插值操作。我们没有修改判决器或者损失函数, 因此,我们的工作与正在进行的有关GAN损失函数,正则化和超参数的讨论正交。
我们的生成器将输入的隐编码嵌入到一个中间的隐空间, 它对变量因素在网络中的表示有更深的影响。输入的隐空间必须服从于训练数据的概率密度, 我们认为这将导致不同程度的不可避免的耦合。 我们的中间隐空间摆脱了这个限制, 因此可以允许解耦。因为此前的评估隐空间解耦程度的方式不能直接适用于我们的方法,我们提出两种新的自动的标准——感知路径长度和线性分离度——为了量化生成器的这些方面。使用这些标准,我们展示了相比与传统地GAN结构,我们的生成器有一个更加线性的,更少耦合的不同变量因素的表征。
最后,我们呈现了一个人脸数据集(Flicker-Face-HQ, FFHQ)。
2. Style-based generator
传统地, 隐编码由生成器通过一个输入层提供, 比如第一层是一个前向传播网络(如图1a)。 我们通过删除输入层抛弃这种设计, 并且用一个学习到的常数开始来替代(如图1b 右侧)。在输入空间Z里给定一个隐编码z, 一个非线性的映射网络 $f: Z \rightarrow W$ 首先产生 $w \in W$(如图1b 左侧)。 为了简化,我们将两个空间的维度都设为512, 映射函数是一个8层的多层感知机, 将会4.1部分分析这个决定。学习仿射变换将w转化为风格 $y = (y_s, y_b)$ 控制生成网络g在每个卷积层后的自适应实例规范化(AdaIN)操作。AdaIN操作被定义为:
\[AdaIN(x_i, y) = y_{s, i} \frac{x_i - \mu(x_i)}{\sigma(x_i)} + y_{b, i} \tag 1\]其中每层特征映射$x_i$被分别规范化, 然后使用相关的风格y的放缩参数进行放缩和偏置。因此y的维度是那一层特征映射数量的两倍。
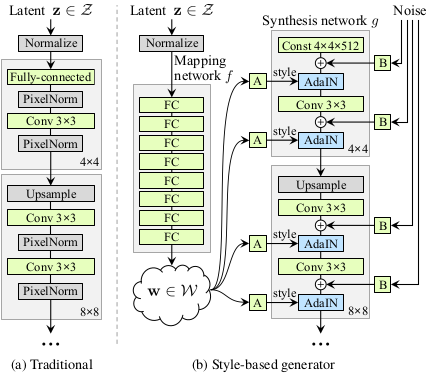
Figure 1: 传统的生成器[28]只通过输入层提供隐编码,我们首先将输入映射到中间隐空间空间W,然后在每个卷积层通过自适应实例规范化(AdaIN)控制生成器。高斯噪声是在每次卷积之后,在计算非线性激活之前加入的。这里“A”表示学习的仿射变换,“B”将学习的 每个通道比例因子 应用于噪声输入。映射网络 $f$ 由8层组成, 生成网络 $g$ 由18层组成, 每个分辨率两层($4^2 - 1024^2$)。 最后一层的输出使用一个单独的 1x1 卷积转换成RGB。 相比于传统的生成器参数为23.1M, 我们的生成器总共有26.2M可训练的参数。
我们的方法和风格迁移相比, 我们从向量w而不是一个样本图片计算空间不变的风格y。我们选择为y重用风格这一说法, 因为它和已经用在的前向风格迁移的结构相似, 无监督地图像到图像的翻译等。与传统地特征迁移相比较,AdaIN非常适合我们的目标,因为它的效率和压缩的表征。
最后,我们通过引入显式噪声输入,为生成器提供了一种生成随机细节的方法。这些是由不相关的高斯噪声组成的单通道图像,我们将噪声图像馈送到生成网络的每一层。噪声图像使用学习到的放缩因子广播到所有特征映射,然后添加到相关卷积的输出, 如图1b所示。添加噪声到输入的影响将会在3.2和3.3部分讨论。
2.1. Quality of generated images
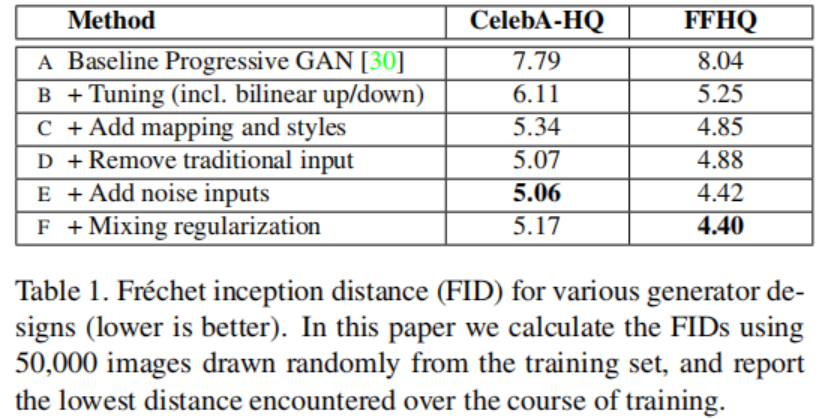
我们的基础配置是Progressive GAN, 从那里我们继承了网络和所有超参数除非另有说明。我们选择了一个有提升的基础通过使用双线性升降采样, 更长的训练时间, 并且微调超参数。在附录C中有细节的描述和训练以及超参数的配置。然后我们通过增加映射网络和AdaIN操作进一步提升了表现, 并且令人惊讶地观察到,网络不再受益于将潜编码输入到第一卷积层中。我们因此通过移除输入层并且从一个学习到的4x4x512的常量Tensor开始合成图像简化网络。我们发现非常值得注意的是,即使综合网络仅通过控制AdaIN操作的样式来接收输入,也能够产生有意义的结果。
最后,我们引入了噪声输入进一步提升了结果, 和新的混合正则化, 它对相邻风格进行解相关,并对生成的图像进行更精细的控制(3.1部分)。
我们使用两种不同的损失函数评估我们的方式:对于CELEBA-HQ使用WGAN-GP, 对FFHQ使用配置A中的WGAN-GP, 以及对B-F使用了$R_1$正则化的不饱和loss。我们的投稿没有修改loss函数。
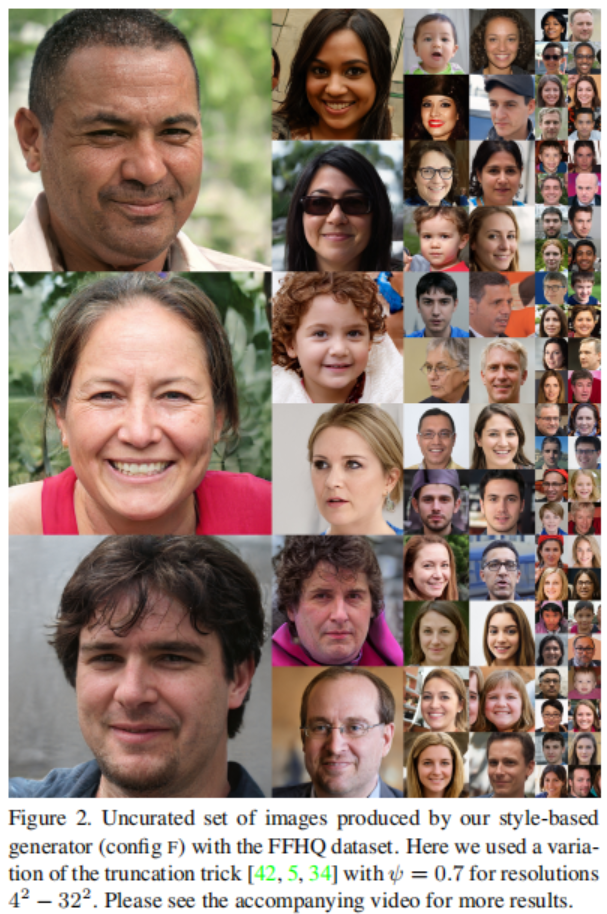

我们观察到基于风格的生成器相较于传统地生成器显著地提高FIDs, 几乎20%。图2展示了一个使用我们的生成器从FFHQ数据集产生的新图像集合。如FIDs证实的那样, 平均质量很高, 即便是眼镜、帽子之类的配饰也成功生成。 对于此图, 我们使用所谓的阶段技巧避免从W的极端区域采样——附录B详细地描述了这个技巧是如何使用B而不是使用Z来执行的。请注意,我们的生成器仅有选择性地应用于低分辨率的截断,因此高分辨率的细节不会受到影响。
这篇文章中所有FIDs都是没有阶段技巧计算出来的, 并且我们仅仅在图2和视频中使用它作为解释性的目的。所有的图像被生成为$1024^2$分辨率。
2.2. Prior art
大部分GAN结构的作品专注于提升判决器, 比如使用多判决器, 多分辨率判决器, 或者自注意力。 在生成器上的作品主要专注于提取输入隐空间的分布或者将输入隐空间塑造成高斯混合模型等。
最近的条件生成器通过单独饿的嵌入网络, 将类别标识送入生成器的许多层, 此时仍然通过输入层提供隐向量。一些作者想要将隐编码的部分送入多个生成器层。 同期的工作中,Chen等人的“self modulate”生成器使用AdaINs, 和我们的工作相似, 但是没有使用中间向量空间或者噪声输入。
3. Properties of the style-based generator
我们的生成器结构通过缩放风格来控制图像生成。映射网络和AdaIN中的仿射变换可以看作是在一个学习到的分布中对每种风格采样的过程, 生成网络基于风格的集合来生成新的图像。网络中局部风格(卷积层+AdaIN)的改变将会影响图片的特定部分。
为什么会有这种局部化, AdaIN操作首先将每个通道规范化为均值为0方差为1, 然后基于风格进行缩放和偏置。新的由风格影响的通道统计数据, 将会修改这些特征对接下来卷积层的重要性, 但是由于规范化,它们不依赖于原始的数据。因此每种风格仅仅控制在被下一个AdaIN操作重写之前的一个卷积层。
3.1. Style mixing
为了进一步鼓励风格进行局部化, 我们使用混合正则化,在训练期间使用两个而不是一个随机潜编码生成一个给定的百分比的图像。当生成这样的一个图像,我们只需在合成网络中随机选择的一点,从一个潜编码切换到另一个潜编码(我们称为风格混合的操作)。具体来说,我们通过映射网络运行两个潜编码z1,z2,并让相应的w1,w2控制风格,w1适用于交叉点之前,w2适用于交叉点之后。 此正则化技术可防止网络相邻风格相关。
表2展示了在训练期间使用混合正则化如何显著改善局部化, 在测试时多个隐向量混合, 提升的FIDs所表示的那样。图3展示了在不同尺度通过混合两个隐编码合成的图像样例。我们可以看到每个风格的子集控制图像的有意义的高级特征。
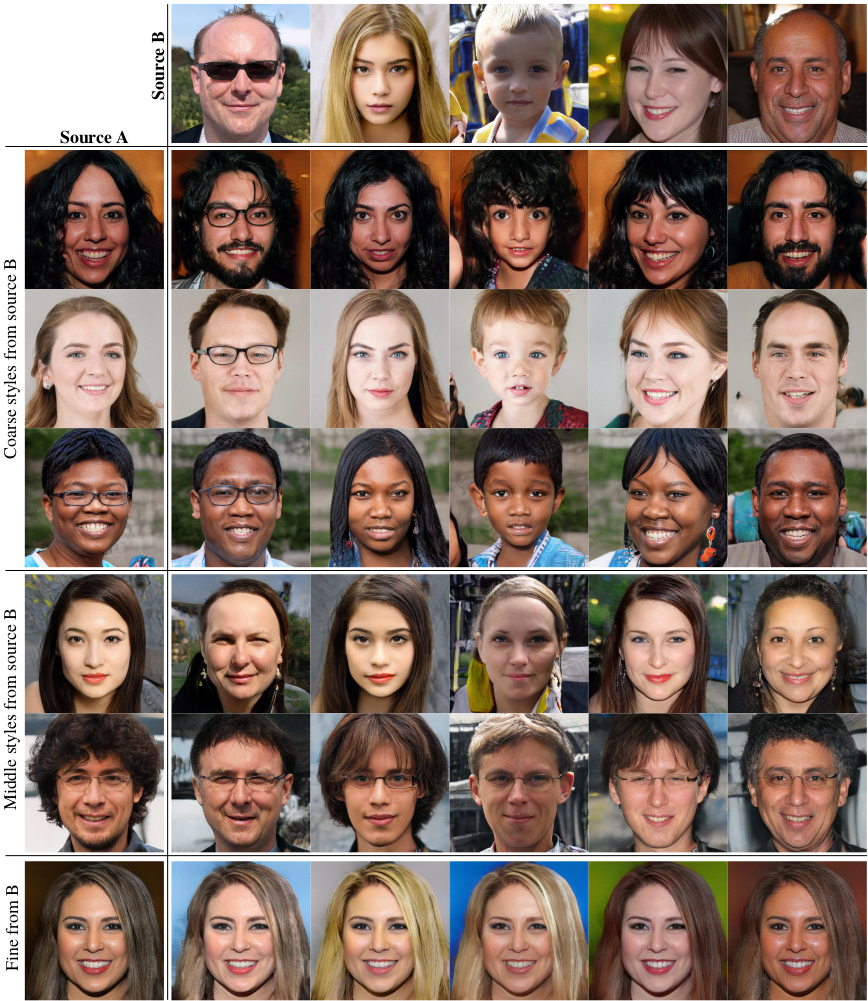

Figure 3. 从它们各自的隐编码(源A和源B)生成两组图像;其余图像是通过从源B复制指定风格子集并从源a获取其余风格来生成的。复制低分辨率($4^2 - 8^2$)相关的风格会带来来自B的高层次的风格, 比如姿势, 头发风格, 脸的形状、以及眼镜, 而所有的颜色(眼睛、头发、光照)以及更精细的脸部特征来自A。 如果从B中复制中等分辨率大小($16^2 - 32^2$)的风格, 我们将从 B 继承较小尺度的面部特征、发型、睁眼/闭眼, 而保留A的姿势、面部形状以及眼镜。最后, 从B复制更精细的分辨率 $24^2 - 1024^2$的风格 主要带来色彩的变化以及更微小的变化。
3.2. Stochastic variation
人类特点的很多方面可以被认为是随机的, 比如头发的位置, 胡子茬, 雀斑, 活着皮肤毛孔。只要遵循正确的分布,这些中的任何一个都可以随机化而不会影响我们对图像的感知。
让我们来考虑一下传统的生成器是如何执行这些随机变化的。假定对网络的唯一输入是通过输入层,则网络需要发明一种方法,以便在需要时从较早的激活中生成空间变化的伪随机数。这会消耗网络的容量,并且隐藏生成信号的周期性是很困难的, 并且并不总是成功的, 如生成图像中常见的重复图案证明的那样。我们的结构回避这些问题通过在每个卷积之后增加每像素的噪声。
图4展示了相同基础图像的随机实现,由使用了我们生成器加上不同噪声产生实现。我们可以看到,噪声仅仅影响随机的部分, 保持整体组成和高级方面(如身份)不变。图5进一步解释了使用不同变量给不同层的子集的影响。


我们发现这很有趣,噪声的影响紧紧出现在网络局部化的部分。我们假设生成器的任意一点,有一种尽快引入新内容的压力,并且对于我们网络最简单的方式是依赖于噪声提供的随机变量。每层都有一组新的噪声,因此没有动机从较早的激活中产生随机效应,从而导致局部效应。
3.3. Separation of global effects from stochasticity
前面的部分展示了当风格改变时有全局的影响(改变姿势,身份等), 噪声仅影响无关紧要的随机变化(头发,胡须等的不同)。此观察结果与风格转换文献相符,在文献中已确定空间不变的统计信息(Gram矩阵,通道级别的均值,方差等)可靠地编码图像的风格当空间变化特征编码为一个特定的实例。
在我们基于风格的生成器中,风格影响整个图像因为完整的特征映射用同样的值放缩和偏置。因此,可以连贯地控制诸如姿势,照明或背景风格之类的全局效果。同时,噪声被独立地添加到每个像素,因此理想地适合于控制随机变化。如果网络试图使用噪声来控制例如姿势,则将导致空间上不一致的决定,然后判别器将对其进行惩罚。因此,网络会在没有明确指导的情况下学会适当地使用全局和局部通道。
B. Truncation trick in W
如果我们考虑训练数据的分布,很明显低密度区域很难去表示,因此生成器可能很难学习。这是在所有生成模型技术中的一个重要的开放问题。但是,从截断的或其他缩小的采样空间中提取隐向量往往会改善平均图像质量,尽管会损失一些变化。
我们遵循相似的策略。首先,我们计算大部分 $W$ 的中心为 $\bar w = E_{z \thicksim P(z)}[f(z)]$。在FFHQ的情况下,该点表示某种平均面孔(图8,ψ= 0)。我们可以从中心放缩一个给定w的偏差 $w’ = \bar w + \psi(w - \bar w)$, 其中$\psi < 1$

C. Hyperparameters and training details
我们基于Progressive GANs的官方实现建立模型,我们继承了大部分的训练细节。原始的设置如表1中配置A。尤其是,我们使用了相同的判决器结构, 与分辨率有关的小批量尺寸,Adam超参数以及生成器的指数移动平均值。我们对CELEBA-HQ和FFHQ使用了镜像数据增强, 但是对LSUN没有使用。我们的训练时间大约是在8个特斯拉V100上训练了一周。
对于我们提升的基准模型(表1中的配置B),我们为了提升结果的质量做了一些改动。我们将两个网络中最邻近升/降采样替换为双线性采样, 我们通过在每个上采样层之后和每个下采样层之前对激活进行低通滤波来实现。我们和Progressive GANs一样的方式使用渐进增长, 但是从$8^2$分辨率开始。 对FFHQ数据集, 我们将WGAN-GP替换成了使用$\gamma = 10$的$R_1$正则化的不饱和loss。 使用了$R_1$正则化, 我们发现FID分数持续下降很长一段时间相比于WGAN-GP, 因此我们增加了训练时间从12M的图片到25M的图片。对于FFHQ数据集, 我们使用了和Progressive GANs相同的学习率, 但是我们发现对于CelebA-HQ在分辨率为$512^2$和$1024^2$时将学习率调整为0.002训练更加稳定。
对与基于风格的生成器(表1中的配置F), 我们对所有层使用参数$\alpha = 0.2$的leaky ReLU和均衡学习率。我们的映射网络由8个全连接层组成,所有输入和输出激活的维度(包括z和w)都是512。我们发现增加映射网络的深度在有高的学习率的情况下会使训练不稳定。因此我们为映射网络减小两倍规模的学习率, 比如$\lambda’ = 0.01·\lambda$。 我们使用标准正态分布$N(0, 1)$初始化所有的卷积层, 全连接层, 和仿射变换层参数。生成网络的常量输入初始化为1。 偏置和噪声放缩因子初试化为0, 除了和$y_s$相关的偏置被初始化为1。
在我们的网络中不使用批规范化, 谱规范化, 注意力机制, dropout, 或者像素级别特征向量的规范化。
实验部分
双重反向传播(梯度惩罚)
BlurFunctionBackward::backward is for double backprop. (gradient penalty) So it is actually used.
The major difference is that when using Blur you don’t need gradients for kernels. It seems like that gradients for blur kernel is calculated even when requires_grad of kernel is False. So using custom function is significantly faster for Blur double backprop.
running average of generator
In progressive gan paper author used running average of generator when infer samples. accumulate() calculates running average and save average to g_running.
引入相关包
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import init
from torch.nn import functional as F
from torch.autograd import Function
from math import sqrt
import random
权重初始化
线性层使用xavier初始化
1
2
3
def init_linear(linear):
init.xavier_normal(linear.weight)
linear.bias.data.zero_()
卷积层使用kaiming初始化
1
2
3
4
def init_conv(conv, glu=True):
init.kaiming_normal(conv.weight)
if conv.bias is not None:
conv.bias.data.zero_()
均衡学习率
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
class EqualLR:
def __init__(self, name):
self.name = name
def compute_weight(self, module):
weight = getattr(module, self.name + '_orig')
fan_in = weight.data.size(1) * weight.data[0][0].numel()
return weight * sqrt(2 / fan_in)
# 这里的module是conv/linear
@staticmethod
def apply(module, name):
# 这一步仅仅执行了__init__以及实例化了一个对象
fn = EqualLR(name)
weight = getattr(module, name)
# 这里把module(也就是conv/linear)的weight参数删掉了
del module._parameters[name]
# 这里把原来的权重注册进去,新的权重没有注册吗?
# 新的权重在调用fn的时候注册, 也就是调用__call__的时候
module.register_parameter(name + '_orig', nn.Parameter(weight.data))
module.register_forward_pre_hook(fn)
# module和fn到底是什么关系?
return fn
# 这里的module是fn
def __call__(self, module, input):
weight = self.compute_weight(module)
setattr(module, self.name, weight)
def equal_lr(module, name='weight'):
EqualLR.apply(module, name)
return module
混淆升/降采样采样
这里为什么这样做,我还不太懂。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
class FusedUpsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, padding=0):
super().__init__()
weight = torch.randn(in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, kernel_size)
bias = torch.zeros(out_channel)
fan_in = in_channel * kernel_size * kernel_size
self.multiplier = sqrt(2 / fan_in)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(weight)
self.bias = nn.Parameter(bias)
self.pad = padding
def forward(self, input):
# relu的kaiming_normal
weight = F.pad(self.weight * self.multiplier, [1, 1, 1, 1])
weight = (
weight[:, :, 1:, 1:]
+ weight[:, :, :-1, 1:]
+ weight[:, :, 1:, :-1]
+ weight[:, :, :-1, :-1]
) / 4
out = F.conv_transpose2d(input, weight, self.bias, stride=2, padding=self.pad)
return out
class FusedDownsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, padding=0):
super().__init__()
weight = torch.randn(out_channel, in_channel, kernel_size, kernal_size)
bias = torch.zeros(out_channel)
fan_in = in_channel * kernel_size * kernel_size
self.multiplier = sqrt(2 / fan_in)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(weight)
self.bias = nn.Parameter(bias)
self.pad = padding
def forward(self, input):
weight = F.pad(self.weight * self.multiplier, [1, 1, 1, 1])
weight = (
weight[:, :, 1:, 1:]
+ weight[:, :, :-1, 1:]
+ weight[:, :, 1:, :-1]
+ weight[:, :, :-1, :-1]
) / 4
out = F.conv2d(input, weight, self.bias, stride=2, padding=self.pad)
return out
像素级别的规范化
在论文中是去掉了pixelnorm的, 它用在了输入高斯噪声的第一层, 也就是八个线性层之前。
1
2
3
4
5
6
class PixelNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, input):
return input / torch.sqrt(torch.mean(input ** 2, dim=1, keepdim=True) + 1e-8)
模糊降采样
作者说这里求两次梯度,是为了梯度惩罚。
不明白。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
class BlurFunctionBackward(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, grad_output, kernel, kernel_flip):
ctx.save_for_backward(kernel, kernel_flip)
grad_input = F.conv2d(grad_output, kernel_flip, padding=1, groups=grad_output.shape[1])
return grad_input
# 求二次梯度,用于梯度惩罚
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, gradgrad_output):
kernel, kernel_flip = ctx.saved_tensors
grad_input = F.conv2d(gradgrad_output, kernel, padding=1, groups=gradgrad_output.shape[1])
return grad_input, None, None
class BlurFuction(Function):
@staticmethod
def forward(ctx, input, kernel, kernel_flip):
ctx.save_for_backward(kernel, kernel_flip)
output = F.conv2d(input, kernel, padding=1, groups=input.shape[1])
return output
@staticmethod
def backward(ctx, grad_output):
kernel, kernel_flip = ctx.saved_tensors
grad_input = BlurFunctionBackward.apply(grad_output, kernel, kernel_flip)
return grad_input, None, None
blur = BlurFuction.apply
class Blur(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel):
super().__init__()
weight = torch.tensor([[1, 2, 1], [2, 4 ,2], [1, 2, 1]], dtype=torch.float32)
weight = weight.view(1, 1, 3, 3)
weight = weight / weight.sum()
# 对最后两维进行行和列的翻转
weight_flip = torch.flip(weight, [2, 3])
# 根据通道数,复制多个卷积核
self.register_buffer('weight', weight.repeat(channel, 1, 1, 1))
self.register_buffer('weight_flip', weight_flip.repeat(channel, 1, 1, 1))
def forward(self, input):
return blur(input, self.weight, self.weight_flip)
均衡学习率的卷积层和线性层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
class EqualConv2d(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__()
conv = nn.Conv2d(*args, **kwargs)
conv.weight.data.normal_()
conv.bias.data.zero_()
self.conv = equal_lr(conv)
def forward(self, input):
return self.conv(input)
class EqualLinear(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_dim, out_dim):
super().__init__()
linear = nn.Linear(in_dim, out_dim)
linear.weight.data.normal_()
linear.bias.data.zero_()
self.linear = equal_lr(linear)
def forward(self, input):
return self.linear(input)
卷积块、风格卷积块、AdaIN等
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
class ConvBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, padding, kernel_size2=None, padding2=None, downsample=False, fused=False):
super().__init__()
pad1 = padding
pad2 = padding
if padding2 is not None:
pad2 = padding2
kernel1 = kernel_size
kernel2 = kernel_size
if kernel_size2 is not None:
kernel2 = kernel_size2
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
EqualConv2d(in_channel, out_channel, kernel1, padding=pad1),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
)
if downsample:
if fused:
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
Blur(out_channel),
# 为什么混淆降采样步长为2
FusedDownsample(out_channel, out_channel, kernel2, padding=pad2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
)
else:
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
Blur(out_channel),
# 而卷积步长为1且池化?
EqualConv2d(out_channel, out_channel, kernel2, padding=pad2),
nn.AvgPool2d(2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
)
else:
self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
EqualConv2d(out_channel, out_channel, kernel2, padding=pad2),
nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
)
def forward(self, input):
out = self.conv1(input)
out = self.conv2(out)
return out
class AdaptiveInstanceNorm(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, style_dim):
super().__init__()
self.norm = nn.InstanceNorm2d(in_channel)
self.style = EqualLinear(style_dim, in_channel * 2)
self.style.linear.bias.data[:in_channel] = 1
self.style.linear.bias.data[in_channel:] = 0
def forward(self, input, style):
# 添加第三维和第四维,用于广播
style = self.style(style).unsqueeze(2).unsqueeze(3)
# 将第一维分成两个tensor,
gamma, beta = style.chunk(2, 1)
out = self.norm(input)
out = gamma * out + beta
return out
class NoiseInjection(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel):
super().__init__()
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(1, channel, 1, 1))
def forward(self, image, noise):
return image + self.weight * noise
class ConstantInput(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channel, size=4):
super().__init__()
self.input = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, channel, size, size))
def forward(self, input):
batch = input.shape[0]
out = self.input.repeat(batch, 1, 1, 1)
return out
class StyleConvBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size=3, padding=1, style_dim=512, initial=False, upsample=False, fused=False):
super().__init__()
if initial:
self.conv1 = ConstantInput(in_channel)
else:
if upsample:
if fused:
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
FusedUpsample(
in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, padding=padding),
Blur(out_channel)
)
else:
self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest'),
EqualConv2d(
in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, padding=padding
),
Blur(out_channel)
)
else:
self.conv1 = EqualConv2d(
in_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, padding=padding
)
self.noise1 = equal_lr(NoiseInjection(out_channel))
self.adain1 = AdaptiveInstanceNorm(out_channel, style_dim)
self.lrelu1 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
self.conv2 = EqualConv2d(out_channel, out_channel, kernel_size, padding=padding)
self.noise2 = equal_lr(NoiseInjection(out_channel))
self.adain2 = AdaptiveInstanceNorm(out_channel, style_dim)
self.lrelu2 = nn.LeakyReLU(0.2)
def forward(self, input, style, noise):
out = self.conv1(input)
out = self.noise1(out, noise)
out = self.lrelu1(out)
out = self.adain1(out, style)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.noise2(out, noise)
out = self.lrelu2(out)
out = self.adain2(out, style)
return out
生成器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
# 这里的生成器利用风格升采样产生图像
class Generator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, code_dim, fused=True):
super().__init__()
self.progression = nn.ModuleList(
[
StyleConvBlock(512, 512, 3, 1, initial=True), # 4
StyleConvBlock(512, 512, 3, 1, upsample=True), #8
StyleConvBlock(512, 512, 3, 1, upsample=True), # 16
StyleConvBlock(512, 512, 3, 1, upsample=True), # 32
StyleConvBlock(512, 256, 3, 1, upsample=True), #64
StyleConvBlock(256, 128, 3 ,1, upsample=True, fused=fused), #128
StyleConvBlock(128, 64, 3, 1, upsample=True, fused=fused), #256
StyleConvBlock(64, 32, 3, 1, upsample=True, fused=fused), #512
StyleConvBlock(32, 16, 3, 1, upsample=True, fused=fused), #1024
]
)
self.to_rgb = nn.ModuleList(
[
EqualConv2d(512, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(512, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(512, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(512, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(256, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(128, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(64, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(32, 3, 1),
EqualConv2d(16, 3, 1)
]
)
def forward(self, style, noise, step=0, alpha=-1, mixing_range=(-1, -1)):
out = noise[0]
if len(style) < 2:
# inject_index是用来干什么的?
# inject_index: 10
inject_index = [len(self.progression) + 1]
else:
# style = 2
# 从[0, step)选出不重复的len(style)-1个
inject_index = random.sample(list(range(step)), len(style) - 1)
# crossover又是做什么用的?
#
crossover = 0
for i, (conv, to_rgb) in enumerate(zip(self.progression, self.to_rgb)):
if mixing_range == (-1, -1):
# inject_index[crossover]
if crossover < len(inject_index) and i > inject_index[crossover]:
crossover = min(crossover + 1, len(style))
style_step = style[crossover]
else:
# mixing_range[0]: 0
# mixing_range[1]: 1
# 当i为0和1时使用source的style
# 其它时候使用target的style
if mixing_range[0] <= i <= mixing_range[1]:
style_step = style[1]
else:
style_step = style[0]
if i > 0 and step > 0:
out_prev = out
out = conv(out, style_step, noise[i])
# step用于控制到网络哪一层停止
if i == step:
# 通道64->3
out = to_rgb(out)
if i > 0 and 0 <= alpha < 1:
# 上一层的输出上采样后和这层融合
# 用于网络新层和旧层间的过度
skip_rgb = self.to_rgb[i-1](out_prev)
skip_rgb = F.interpolate(skip_rgb, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
out = (1 - alpha) * skip_rgb + alpha * out
break
return out
# Style生成器主要用线性层用于生成风格W
class StyledGenerator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, code_dim=512, n_mlp=8):
super().__init__()
self.generator = Generator(code_dim)
layers = [PixelNorm()]
for i in range(n_mlp):
layers.append(EqualLinear(code_dim, code_dim))
layers.append(nn.LeakyReLU(0.2))
self.style = nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, input, noise=None, step=0, alpha=-1, mean_style=None, style_weight=0, mixing_range=(-1, -1)):
styles = []
if type(input) not in (list, tuple):
input = [input]
for i in input:
styles.append(self.style(i))
batch = input[0].shape[0]
if noise is None:
noise = []
for i in range(step + 1):
size = 4 * 2 ** i
noise.append(torch.randn(batch, 1, size, size, device=input[0].device))
if mean_style is not None:
styles_norm = []
for style in styles:
styles_norm.append(mean_style + style_weight * (style - mean_style))
styles = styles_norm
return self.generator(styles, noise, step, alpha, mixing_range=mixing_range)
def mean_style(self, input):
style = self.style(input).mean(0, keepdim=True)
return style
判决器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
class Discriminator(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, fused=True, from_rgb_activate=False):
super().__init__()
self.progression = nn.ModuleList(
[
ConvBlock(16, 32, 3, 1, downsample=True, fused=fused), # 512
ConvBlock(32, 64, 3, 1, downsample=True, fused=fused), # 256
ConvBlock(64, 128, 3, 1, downsample=True, fused=fused), # 128
ConvBlock(128, 256, 3, 1, downsample=True, fused=fused), # 64
ConvBlock(256, 512, 3, 1, downsample=True), # 32
ConvBlock(512, 512, 3, 1, downsample=True), # 16
ConvBlock(512, 512, 3, 1, downsample=True), # 8
ConvBlock(512, 512, 3, 1, downsample=True), # 4
ConvBlock(513, 512, 3, 1, 4, 0),
]
)
def make_from_rgb(out_channel):
if from_rgb_activate:
return nn.Sequential(EqualConv2d(3, out_channel, 1), nn.LeakyReLU(0.2))
else:
return EqualConv2d(3, out_channel, 1)
self.from_rgb = nn.ModuleList(
[
make_from_rgb(16),
make_from_rgb(32),
make_from_rgb(64),
make_from_rgb(128),
make_from_rgb(256),
make_from_rgb(512),
make_from_rgb(512),
make_from_rgb(512),
make_from_rgb(512),
]
)
self.n_layer = len(self.progression)
self.linear = EqualLinear(512, 1)
def forward(self, input, step=0, alpha=-1):
# step, step-1, ..., 0
for i in range(step, -1, -1):
# index用于控制使用倒数哪几层
index = self.n_layer - i - 1
if i == step:
out = self.from_rgb[index](input)
if i == 0:
out_std = torch.sqrt(out.var(0, unbiased=False) + 1e-8)
mean_std = out_std.mean()
mean_std = mean_std.expand(out.size(0), 1, 4, 4)
out = torch.cat([out, mean_std], 1)
out = self.progression[index](out)
if i > 0:
if i == step and 0 <= alpha < 1:
skip_rgb = F.avg_pool2d(input, 2)
skip_rgb = self.from_rgb[index + 1](skip_rgb)
out = (1 - alpha) * skip_rgb + alpha * out
out = out.squeeze(2).squeeze(2)
out = self.linear(out)
return out
inference
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
import argparse
import math
import torch
from torchvision import utils
@torch.no_grad()
def get_mean_style(generator, device):
mean_style = None
for i in range(10):
style = generator.mean_style(torch.randn(1024, 512).to(device))
if mean_style is None:
mean_style = style
else:
mean_style += style
mean_style /= 10
return mean_style
@torch.no_grad()
def sample(generator, step, mean_style, n_sample, device):
image = generator(
torch.randn(n_sample, 512).to(device),
step=step,
alpha=1,
mean_style=mean_style,
style_weight=0.7,
)
return image
@torch.no_grad()
def style_mixing(generator, step, mean_style, n_source, n_target, device):
source_code = torch.randn(n_source, 512).to(device)
target_code = torch.randn(n_target, 512).to(device)
shape = 4 * 2 ** step
alpha = 1
images = [torch.ones(1, 3, shape, shape).to(device) * -1]
source_image = generator(
source_code, step=step, alpha=alpha, mean_style=mean_style, style_weight=0.7
)
target_image = generator(
target_code, step=step, alpha=alpha, mean_style=mean_style, style_weight=0.7
)
images.append(source_image)
for i in range(n_target):
image = generator(
# taget_code[i].size: (n_source, 512)
[target_code[i].unsqueeze(0).repeat(n_source, 1), source_code],
step=step,
alpha=alpha,
mean_style=mean_style,
style_weight=0.7,
mixing_range=(0, 1),
)
images.append(target_image[i].unsqueeze(0))
images.append(image)
images = torch.cat(images, 0)
return images
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--size', type=int, default=256, help='size of the image')
parser.add_argument('--n_row', type=int, default=3, help='number of rows of sample matrix')
parser.add_argument('--n_col', type=int, default=5, help='number of columns of sample matrix')
parser.add_argument('--path', type=str, default='./stylegan-256px-new.model', help='path to checkpoint file')
args = parser.parse_known_args()[0]
device = 'cuda'
generator = StyledGenerator(512).to(device)
generator.load_state_dict(torch.load(args.path)['g_running'])
generator.eval()
mean_style = get_mean_style(generator, device)
step = int(math.log(args.size, 2)) - 2
img = sample(generator, step, mean_style, args.n_row * args.n_col, device)
utils.save_image(img, 'sample.png', nrow=args.n_col, normalize=True, range=(-1, 1))
for j in range(20):
img = style_mixing(generator, step, mean_style, args.n_col, args.n_row, device)
utils.save_image(
img, f'sample_mixing_{j}.png', nrow=args.n_col + 1, normalize=True, range=(-1, 1)
)
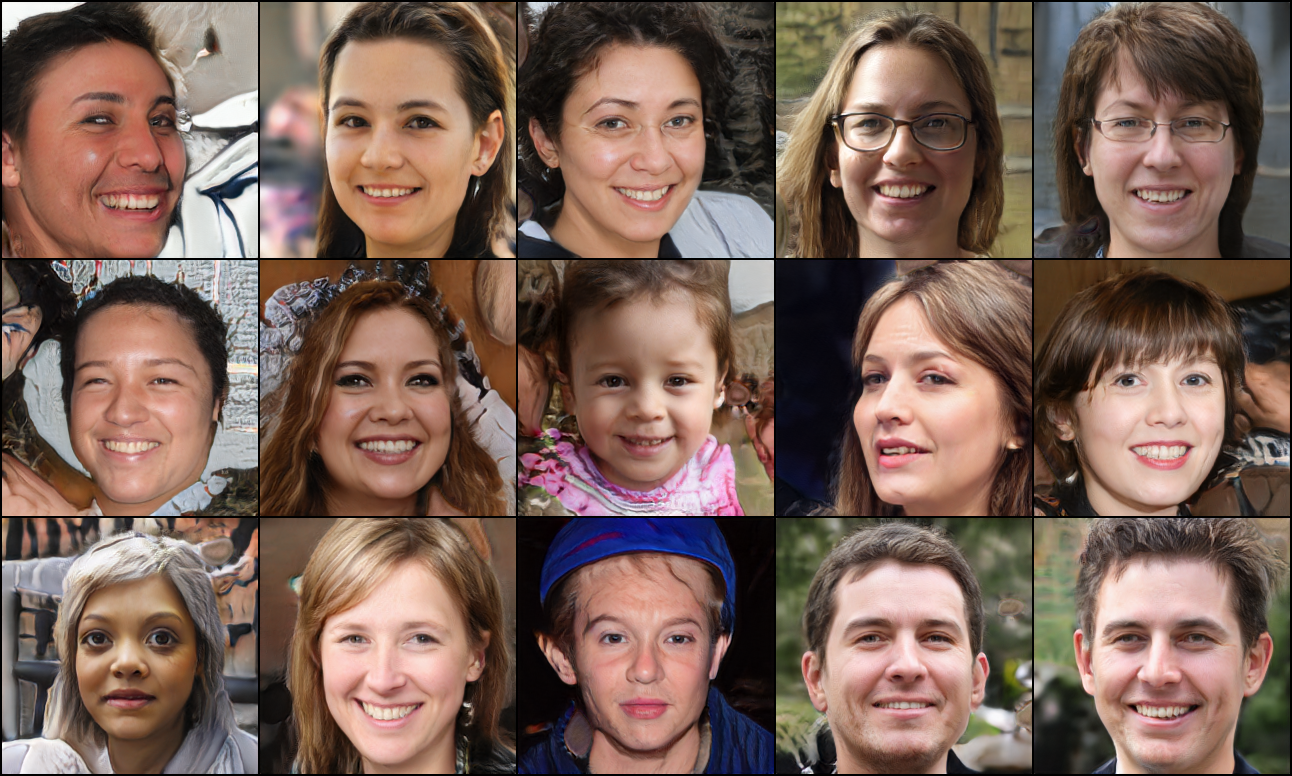
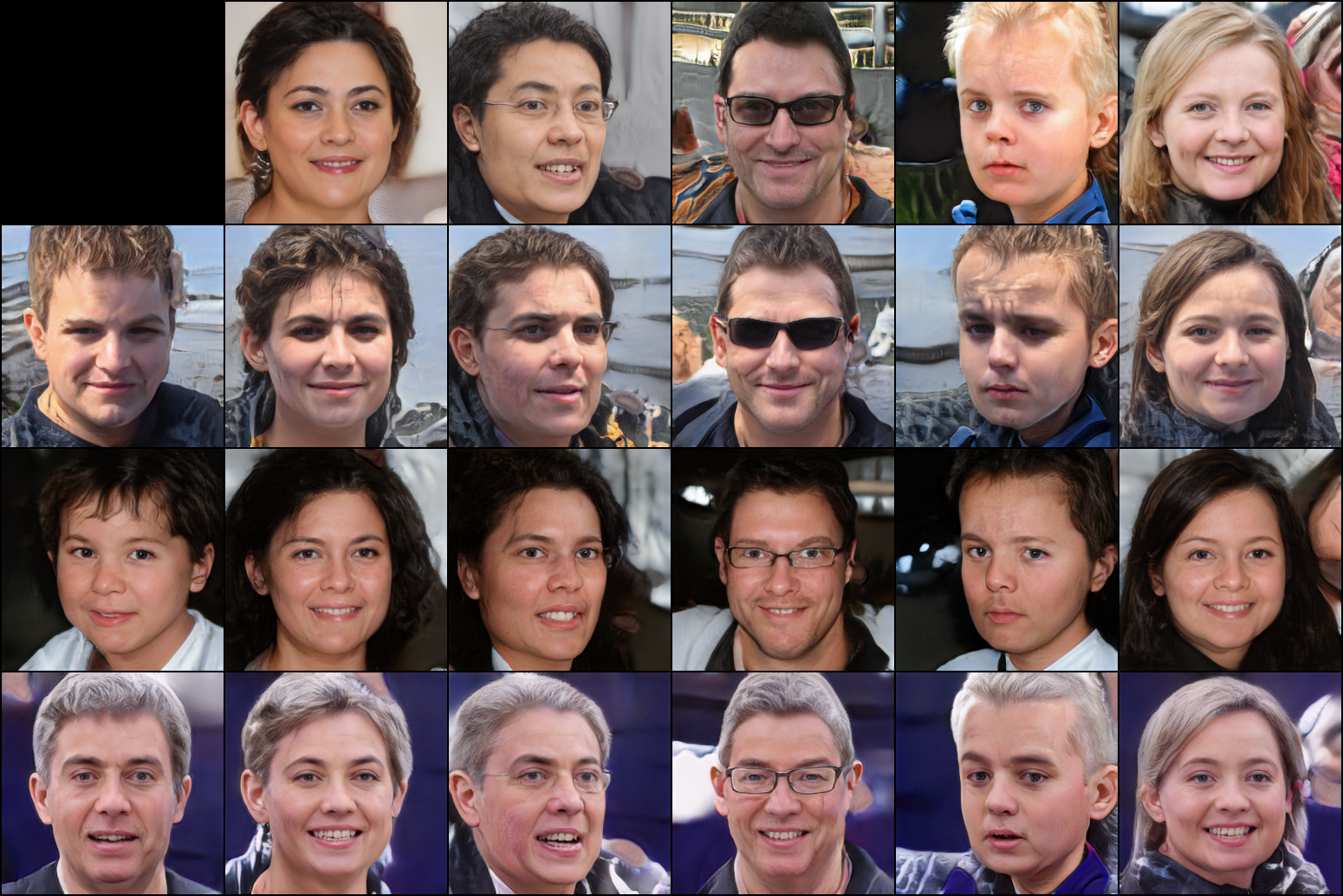
实验结果


Reference
- Karras T, Laine S, Aila T. A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2019: 4401-4410.
- Is BlurFunctionBackward necessary? #89
- accumulate() function ??
- rosinality/style-based-gan-pytorch